Protein Shakes
Whey protein shakes are very common in today’s market place. I wanted to explain one type of protein shake in particular, Muscle Milk. I’m sure you’ve seen it, either at GNC, online, at your gym, or some gas stations even have Muscle Milk you can buy. Since so many people are asking me question about it, I did some research so you can make an informed decision on whether or not it is best for you.
Whey Protein:
Think of milk for example. Milk has a protein breakdown which is 80% casein, 20% whey.
Whey protein has the highest biological value, which means that it is absorbed and used in the body very well, better than a lot of other forms of protein! Whey protein also contains important amino acids that are valuable for protein synthesis (forming muscle).
There are various forms of “whey protein” in shakes and supplements on the market, I want to explain the differences:
1. Milk Protein Concentrates (MPCs)-
It is an ultra-filtered milk, basically powdered skim milk. Milk Protein Concentrates have the same concentration of casein and whey as a normal glass of milk. (80-82% casein protein, 18-20% whey protein). If your protein shake contains MPC as the main source of protein, then you don’t need it. Just drink regular milk. (GNC Lean Shakes use this). MPCs contain a total of 40-89% proteins.
2. Whey Protein Isolates (Whey Isolates)-
Isolates contain 90-94% pure protein. This is better quality protein. The whey is pasteurized which makes it drinkable for people with lactose intolerance, because the lactose (milk sugars) have been removed.
3. Whey Protein Hydrolysates (Hydrolyzed Whey Protein)-
A whey protein that has been treated with enzymes to break down the protein into free amino acids and peptides. It is more expensive, used in some infant formulas, some protein shakes or medical supplements.
Casein Protein
Casein is NOT whey protein, but I wanted to explain what it is. Casein protein is absorbed slowly over time, not as quickly as whey protein. Casein makes up the majority of the protein in milk. Casein takes longer to be digested, which slows down the amount of amino acids being released and absorbed, creating a prolonged period of muscle synthesis. This type of protein would be used for people trying to bulk their muscles, to take before going to bed or when they know they will not eat for a long period of time.
How much?
You do not need more than 30 grams or protein at one time. In fact, 20-30 grams of protein is going to the ideal amount necessary for your meals or your post workout recovery. Remember, a recovery shake after a workout should contain a 2:1 or 3:1 ratio of Carbohydrates:Protein.
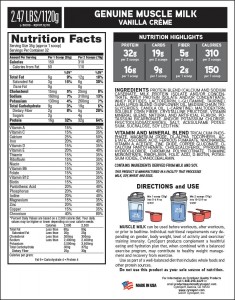
Muscle Milk:
(Pictured to the right)
-This shake contains casein, isolates and concentrates (the concentrates tend to be used to save $, make it cheaper to produce).
-Vegetable Oil: Why do you want to DRINK vegetable oil?
-Crystalline Fructose: Basically sugar.
-Natural & artificial flavors: What does that even mean? It could mean anything! There is no labeling laws for supplements, so it really could mean anything.
-Salt- 430 mg of sodium, yikes! If you are a big hefty man who sweats a LOT, then you may need this much sodium after a workout, most of us get plenty of sodium in our regular diets. Salt is an added ingredient. You should aim for under 1,500-2,000 mg sodium per day! Drinking more than one a day would really put your salt high for the day!
-Sucralose- This is the same artificial sweetener Splenda is made from. I recommend cutting out artificial sugars and using natural sweeteners such as stevia or honey.
-Medium Chain Triglycerides- added to protein drinks to bulk up the calories, often times for people who are trying to gain weight.
-Not a post workout recovery shake- There are too little carbohydrates in this shake to be a real post workout shake. The carb to protein ratio is backwards for these shakes. In a recovery shake there should be two or three times as much carbs as there is protein. This would be more of a meal replacement shake or something drank in the evening for people bulking for muscle growth while sleeping because of the casein protein. Necessary for weight loss? No.
Light Muscle Milk, Ready to Drink:
The main difference I see here is less sugars, no crystalline fructose, and less fat is added, which in turn decreases the calories in the shake (1 gram of fat contains 7 calories, so cutting down on the fat cuts down the calories). The “light” shake is cut come 230 to 160 calories, 9 to 4.5 grams fat, 25 to 20 grams protein. It contains most of the exact same ingredients as described above. (Label is not pictured)
Powders:
(Pictured to the right) The muscle milk powders contain the same ingredients as listed above, but in a powdered form with the water removed. There is still artificial sugars, artificial flavors and vegetable oils. It uses the blend of protein to make a lower priced product, but it does have less salt, so that is good!
Muscle Milk in Summary:
If you are trying to build muscle mass, do not care that there are artificial sugars/flavors and that you are drinking vegetable oil, than you should choose the Muscle Milk Powder over the Ready to Drink bottles. If you are using it as a post workout recovery drink, you should also have a piece of fruit or carbohydrate to increase the carbohydrate:protein ratio. This is not something you would drink if you are trying to lose weight.
